Table of Contents
- What do screw sizes mean?
- Imperial to metric screw conversion chart
- Metric to imperial screw conversion chart
- How to measure a screw size?
- M measurement explained
- M Hexagonal screw measurements
What do screw sizes mean?
Screws are listed in a couple of different ways depending on when and where they were produced. In the UK and Europe, screws are listed in a metric format. Most suppliers will only list the screw sizes in metric, for example, 5 x 70mm. Imperial units used to be used in the UK and are still in use in some countries such as the USA. Screws listed in Imperial units have the length listed in inches and the thread diameter listed by the gauge equivalent (see Imperial to metric screw chart below).
When it comes to the length of screws, the most important thing to consider is the depth of the material that the screw needs to penetrate. If a screw is too long, it will protrude through the material and could potentially cause injury.
 Metric Screws
Metric Screws Imperial Screws
Imperial Screws
Metric Screw Sizes
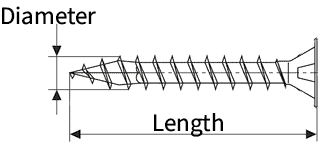
Metric screws are listed by the diameter of the screw thread in millimetres by the length of the screw (in millimetres). The diagram below shows the diameter and length of a screw. For example, 4.5 x 40mm means the screw has a thread diameter (including teeth) of 4.5mm and the length from the head (assuming the head is flat) to the tip of 40mm (see diagram below). If the head is round or will protrude from the surface then the length of the screw is measured from under the head. The length represents the amount of screw screwed into the material.
Imperial Screw Sizes
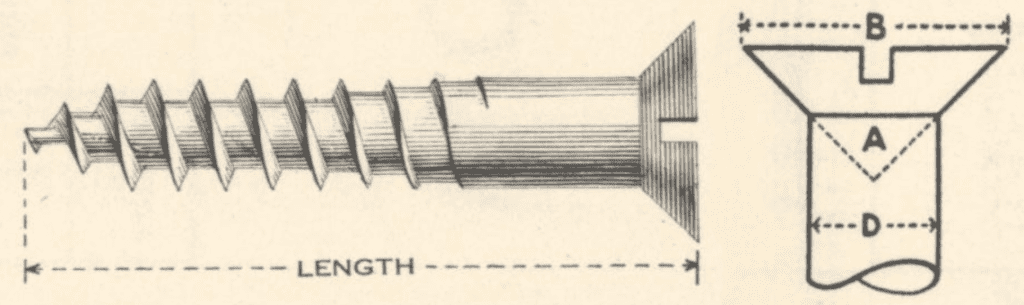
In the case of imperial screws, the sizes are normally presented as the gauge by the length. The length of the screw is given in inches. The gauge represents the diameter of the thread of the screw. In the case of a wood screw with a countersunk head of the type shown in the diagram below, the width of the head of the screw (B) is approximately equal to twice the diameter of the shank of the screw (D). The angle of the countersink in this case (A) is equal to 90°.
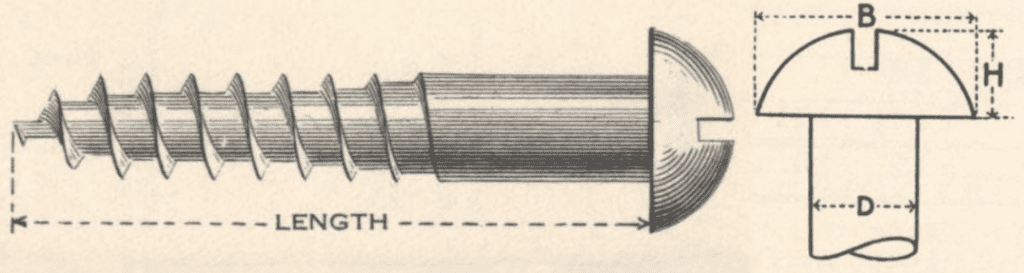
With a round headed screw the length is measured from below the head because the length is classed as the amount of the screw that will be in the material it is screwed into. In the example of the wood screw with a round head shown below, the diameter of the head (B) is approximately equal to twice the diameter of the shank of the screw (D). The depth of the head (H) is approximately equal to 3/4 of the diameter of the shank (D).
Imperial to metric screw conversion chart
| Screw Gauge | Diameter (inches) | Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 4/0 or 0000 | 0.054″ | 1.37 |
| 3/0 or 000 | 0.057″ | 1.45 |
| 2/0 or 00 | 0.060″ | 1.52 |
| 0 | 0.063″ | 1.60 |
| 1 | 0.066″ | 1.68 |
| 2 | 0.080″ | 2.03 |
| 3 | 0.094″ | 2.39 |
| 4 | 0.108″ | 2.74 |
| 5 | 0.122″ | 3.10 |
| 6 | 0.136″ | 3.45 |
| 7 | 0.150″ | 3.81 |
| 8 | 0.164″ | 4.17 |
| 9 | 0.178″ | 4.52 |
| 10 | 0.192″ | 4.88 |
| 11 | 0.206″ | 5.23 |
| 12 | 0.220″ | 5.59 |
| 13 | 0.234″ | 5.94 |
| 14 | 0.248″ | 6.30 |
| 15 | 0.262″ | 6.65 |
| 16 | 0.276″ | 7.01 |
| 17 | 0.290″ | 7.37 |
| 18 | 0.304″ | 7.72 |
| 20 | 0.332″ | 8.43 |
| 22 | 0.360″ | 9.14 |
| 24 | 0.388″ | 9.86 |
| 26 | 0.416″ | 10.57 |
| 28 | 0.444″ | 11.28 |
| 30 | 0.472″ | 11.99 |
| 32 | 0.5″ | 12.70 |
| 36 | 0.556″ | 14.12 |
| 40 | 0.612″ | 15.54 |
Metric to imperial screw conversion chart
Metric screw diameters are usually stepped up in a minimum of 0.5mm. The table below gives a choice of imperial gauges of each of the common millimetre metric diameters.
| Metric Screw Size | Imperial Size | Approximate Equivalent Imperial Gauges |
|---|---|---|
| 3 mm | 0.118″ | 4, 5 |
| 3.5 mm | 0.138″ | 6, 7 |
| 4 mm | 0.157″ | 8 |
| 4.5 mm | 0.177″ | 9 |
| 5 mm | 0.197″ | 10, 11 |
| 6 mm | 0.236″ | 12, 13, 14 |
| 7 mm | 0.276″ | 15, 16, 17 |
| 8 mm | 0.315″ | 18, 20 |
How to measure a screw size?
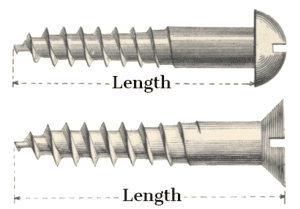
The measurements of a screw typically consist of the diameter by the length. The diameter is usually the diameter of the shank including the thread – the outside thread diameter, this measurement is then presented in millimetres for metric screws or by gauge (see conversion tables above). The length is then defined by the amount of the screw that will be in the end material (e.g. wood). So for example, for a screw with a round head, the length of the screw is measured from below the head to the tip, but for a countersunk head, the length of the screw is measured from the top of the head to the tip. The diagram below gives an example of the difference in length between a countersunk and a round head screw:
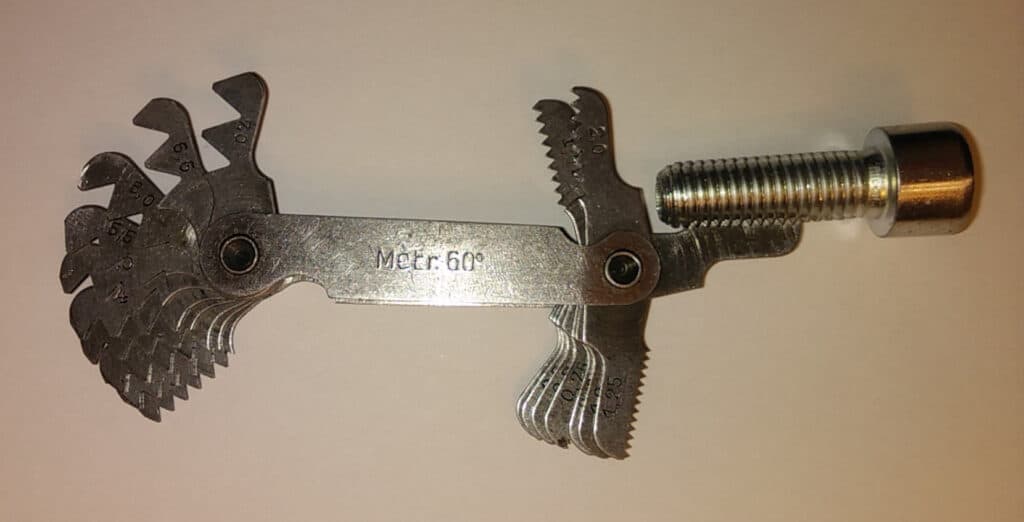
The distance between the teeth is not usually of concern with wood screws but is very important with things like bolts where a matching thread size is required on the nut or material that the bolt is being screwed into. To find out the pitch of a thread you can use a thread gauge. A thread gauge usually consists of numerous strips of metal with various sizes of thread cut into them. To find out the thread size you systematically work your way through the various thread sizes until you find one that matches the pitch of the thread.

M measurement explained
Sometimes the diameter component of a screw can be defined as “M” and a number, for example, M4. Coach screws (lag screws or lag bolts) are normally defined in this way. The sizes are defined by the standard DIN571. Instead of a head that takes a slotted or Phillips type screwdriver, the head of a coach screw is of the hexagonal nut type – see diagram below. Similar to a round head screw the listed length of a coach screw doesn’t include the depth of the head.
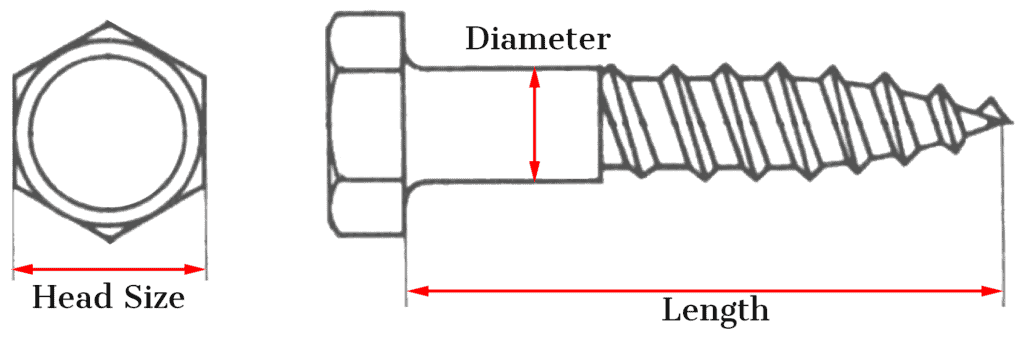
M Hexagonal screw measurements
| M number | Thread Diameter | Head Size / Spanner Size |
|---|---|---|
| M2 | 2mm | 4mm |
| M2.5 | 2.5mm | 5mm |
| M3 | 3mm | 5.5mm |
| M3.5 | 3.5mm | 6mm |
| M4 | 4mm | 7mm |
| M5 | 5mm | 8mm |
| M6 | 6mm | 10mm |
| M7 | 7mm | 12mm |
| M8 | 8mm | 13mm |
| M10 | 10mm | 17mm |
| M12 | 12mm | 19mm |
| M14 | 14mm | 22mm |
| M16 | 16mm | 24mm |
| M18 | 18mm | 27mm |
| M20 | 20mm | 30mm |
| M22 | 22mm | 32mm |
| M24 | 24mm | 36mm |
| M27 | 27mm | 41mm |
| M30 | 30mm | 46mm |
| M33 | 33mm | 50mm |
| M36 | 36mm | 55mm |
| M39 | 39mm | 60mm |
| M42 | 42mm | 65mm |
| M45 | 45mm | 70mm |
| M48 | 48mm | 75mm |
| M52 | 52mm | 80mm |
| M56 | 56mm | 85mm |
| M64 | 64mm | 95mm |
| M72 | 72mm | 105mm |
| M80 | 80mm | 115mm |
What size is an M4 screw?
To use the M4 screw as an example, from the table above we can see that the head size of an M4 screw is 7mm, meaning that a 7mm spanner is required to fit the head of an M4 screw. The diameter of the M4 screw is 4mm – this is the diameter of the thread (including the teeth).

